- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Construction Surveying
*What is setting out?
A definition of setting out is that it is the reverse of surveying. Where as surveying is a process of forming maps and plans of a particular site or area, setting out begins with plans and ends with the various elements of a particular plan correctly positioned on site. Most techniques and equipments used in surveying are also used in setting out. The International organization for standardization (ISO) define setting out as : setting out is the establishment of the marks and lines to define the position and level of elements for the construction work so that works may proceed with reference to them. The process may be contrasted with the purpose of surveying which is to determine by measurement the position of existing features.
*Requirements of setting out:
There are two main requirements when undertaking setting out operations.
- Various elements of the scheme must be correct in all three dimensions both relatively and absolutely that is each must be its correct size, in its correct plan position and correct reduce level.
- Once setting out begins it must proceed quickly with little or no delay in order that the works can proceed smoothly and the cost can be minimized. It must always be remembered that the contractors main commercial purpose is to make a profit -- therefore setting out needs to be done efficiently.
. *Principles of setting out:
The main aim of setting out is to ensure that the various elements of the scheme are positioned correctly in all three dimensions.
*Horizontal Control:
In order that the design of scheme can be correctly fixed in position, it is necessary to establish point on the site which the E, N coordinates are known. These are horizontal control points and once they have been located they can be used with a positioning technique to set out E, N coordinates of the design points.
Two factors for establishing horizontal control points are:
(1) Control points should be located throughout the site in order that all the design points can be fixed from at least two or three of them so that the work can be independently checked.
(2) The design points must be set out to the accuracy stated in the specification.
* Vertical control:
In order that the design points on the works can be positioned at their correct levels, vertical control points of known elevation relative to some specified vertical datum are established. To ordinance data is commonly used and levels on the site are reduced to a nearly OS branch mark.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. What are principles of setting out?
Answer:
First stage setting out:
First stage setting out involves the use of many of the horizontal and vertical control methods and position techniques. The purpose of this stage is to locate the boundaries of the works in their correct position on the ground surface and to define the major clements. In order to this horizontal and vertical control points must be established on or near the site
Second stage setting out:
This setting out continues on from the first stage, beginning at the ground floor slab, road sub base lease level etc. Upto this point, all the control will be outside the main construction, for example, the pegs defining building corners, centre lines and so on will have been knocked out during the earth moving work and on the original control will be undisturbed.
Q2. What is the method of Setting out a pipeline?
Answer:
This operation falls into first category of setting out
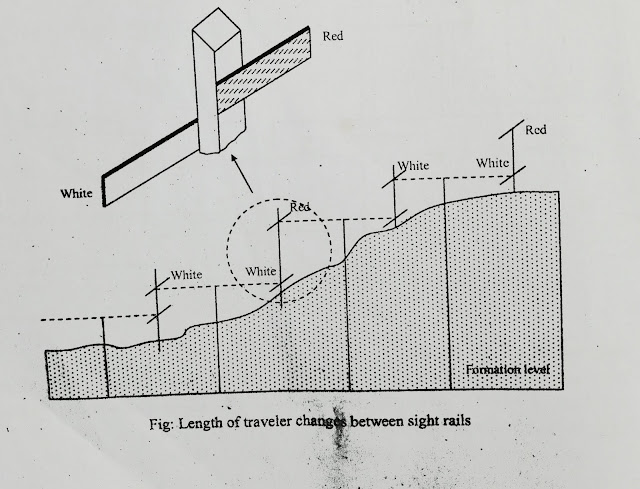
Sight rail for a sewer pipeline:
Sewers normally follow the natural fall in the land and are laid at gradients which induce self cleansing velocity. The figure below shows a sight rail offset at right angles to a pipe line laid in a granular bedding trench.
Horizontal Control:
The drawings will show the directions of the sewer pipes and the positions of the manholes. The line of the sewer is normally pegged at 20 to 30 min intervals using co-ordinate method of positioning from reference points or in relation to existing detail. The direction of line can be sighted using a theodolite and peg.
Vertical control:
It involves the erection of sight rails some convenient height above the inert level of the pipe.
Erection and use of sight rails:
The sight rail uprights are hammered firmly into the ground, usually offset from the line rather than straddling it. Using a near by TBM and levelling equipment, the reduced levels of the tops of the upright. Where the natural slope of the ground is not approximately parallel to the proposed pipe gradient, double sight rails can be used.
Double sight rails:
Often it is required to lay storm water and foul water sewers in adjacent trenches. Since the storm water pipe is usually at a higher level than the former water pipe, it is common to dig one trench to two different levels. Both pipe runs are controlled using different sight rails nailed to the same upright.
Pipe laying:
On completion of excavation, the sight rail control is transferred to pegs in the bottom of trench.
Q3. Write short note about Stacking out a pipeline.
Answer:
1. Sanitary (sewage) sewers and storm sewers which carry storm runoff operate under gravity. The grade in such pipelines is critical. City water, oil and natural gas pipes are not as critical.
2. Location of line is determined after a profile levelling is done.
3. The centre line and offset reference lines are established.
4. Precise alignment and grade are guided by Caser beaus or battered boards.
(A) Cut and fill:
* Centre line and offset line are marked and stationed. The actual profiling and staking are on the offset line, not the centre line.
*Using profile leveling method, obtain ground elevation at each stake, compute the depth of cut or fill to the invert level. .
*Mark that depth on the stake side facing the trench, mark the station on the other side of the stack. .
(B) Line and graph:
Generally done using laser equipment.
Q4. Write short note about Staking out a building.
Answer:
*First step is to locate the building by boundary surveying. Stakes are placed temporarily at the corners as a check.
*In a small size building, a set of batter boards and reference stakes are first set. The boards are around the building corners and nailed at a full number of feet above the . footing base or first floor elevation.
*Nails are driven into the batter boards tops so that a string connecting them will define an outside wall.
Q5. What are the equipments for setting out?
Answer:
Normally ordinary equipments as described before, e.g. levels, theodolites, tapes and EDMI's are used. However, for vertical control Automatic laser levels are being frequently used these days They provide a continuous sharp beam of visible light at a given grade ( selectable by the operator ) and maintain it at the same grade precisely at all times. The laser beam can be intercepted at any point by a special target . This way one knows one's own level without any one giving readings from the instrument end .An extended development of such laser level is to provide a continuously rotating beam with a given grade thereby giving a plane in the same grade . They can be applied for tunnel alignment , machine alignment , elevator shaft alignment , pipe laying , false roofing installation , etc. They expedite placement of grade stakes over large areas suchas airports, parking lots, etc, Laser methods have the advantage of being (i) convenient, (ii) quick, and (iii) accurate. However they are quite expensive. Theodolites combined with EDMIs that can automatically reduce measured slope distances to their horizontal and vertical components and “total – station instruments are also very convenient for construction stakes.
Q6. Write short note about staking out a highway?
Answer:
The staking of a highway project is usually done in the following steps. - 1. The first step is to provide the contractor with stakes showing points marking limits of the construction project. This will enable the contractor to clear the site and hence these stakes are known as clearing stakes. They are 1.5 cm x 2.5 cm x 1.25 m wooden lathe and are placed 1 chain apan.
2. Next, rough cut stakes are to be provided so that the contractor can undertake “rough cut“grading operations.
These stakes are set (i) along the project centre line at 15m interval. (ii) At the beginning and end of all horijontal curves. (iii) At any other grade or alignment transition. The stakes are 2.5 cm x 5.0 cm x 45 cm. On the stakes are marked C or F indicating cut or fill.
3. To guide a contractor in marking final excavations and embankments slope stakes are driven at the slope intercepts (intersections of the original ground and each side slope) or off set a short distance perhaps a meter.
Grade stakes are set at points that have the same ground and grade elevation. Three transition sections normally occur in passing from cut to fill and a grade stake is set at each one



Comments
Post a Comment