ELECTRONIC DISTANCE MEASUREMENT ( EDM ) , CLASSIFICATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION , BASIC PRINCIPLE OF EDM,
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
ELECTRONIC DISTANCE MEASUREMENT (EDM)
Definition:-
Electronic distance measuring instruments measure distance by electromagnetic energy between two points .
BASIC CONCEPT
Time taken for an alternating current to go through one complete cycle of values is called period of the wave. One cycle of the wave motion is completed and the number of cyocles per unit of time is called frequency. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz) which is one cycle per second. The linear length 7 of a wave is wavelength which is a function of frequencyf and the velocity of electromagnetic radiation C as y = C/f . Oscillators convert DC drawn from an energy source into an AC of continuous sine waves. The process of superimposing the desired sine wave or other periodic signal on to the carrier wave is called modulation .
Three main types of modulation
(1) Amplitude modulation
(2) Frequency modulation
(3) Phase modulation.
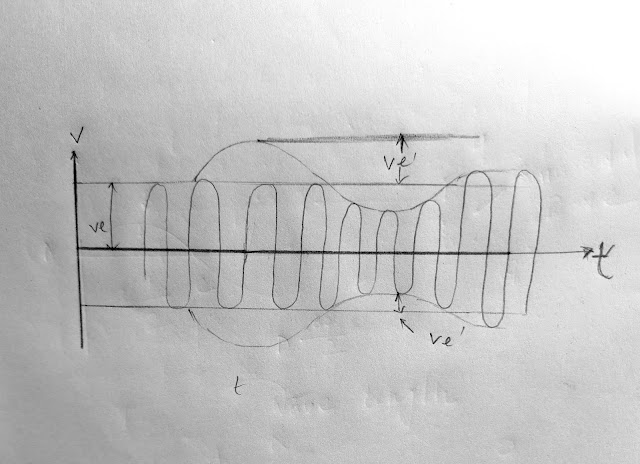
In amplitude modulation, the frequency and the phase of the carrier wave do not change but the strength and amplitude of the carrier wave, V = V sin w .t alternates sinusoidally degree of modulation. It is defined as Ve velv, where V. is the amplitude of modulation wave.
In frequency modulation the amplitude of the carrier wave is kept constant but the frequency varies according to the amplitude and polarity of the modulation signal. The carrier frequency is increased during one half cycle of the modulation signal and decreased during the other half cycle; thus the frequency is least positive and highest when the modulation is most positive.
In phase modulation as in frequency modulation the amplitude of the carrier wave remains constant but the phase of the carrier wave is varied according to the phase of the modulation wave.
Classification of Electromagnetic Radiation
Total spectrum of electromagnetic radiation used in electronic and electro optical distance measurements encompasses wavelengths from the visible light of about 5(10-⁷) to about 3(10⁴)m at the radio frequency region. Frequencies are large numbers and gion, F always negative powers of the basic unit.
Basic principle of EDM
In measuring the distance between two points electronically, an alternating signal travels from one point to the other, it is reflected or returned in same manner and then is compared with the phase of the original signal to determine the travel time for the round trip. If the distance is to be measured by direct time comparison with an accuracy corresponding to the nearest cm, a time of approximately 67 (10-¹²) Sec must be distinguishable. This interval of time is difficult to measure directly but it can be resolved by a phase measurement of a signal with a period for direct transmission, so a much higher carrier frequencies employed and the signal appears as a modulation frequency. Depending on the type of carrier wave employed, EDM instrument can be classified as,
1) Microwave instrument
2) Visible light instrument
3) Infrared instrument
Light frequencies permit the use of optical corner reflectors at the section stations but require an optically clear path between two stations. Microwave systems can operate through fog and clouds although an optically clear path is required if the vertical angle between two stations must be determined to convert into a horizontal distance. The presence of fog or clouds may cause a loss in accuracy and prevent a reliable estimate.
From matrix
BASIC PRINCIPLE OF EDM
CLASSIFICATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
ELECTRONIC DISTANCE MEASUREMENT ( EDM )
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Comments
Post a Comment